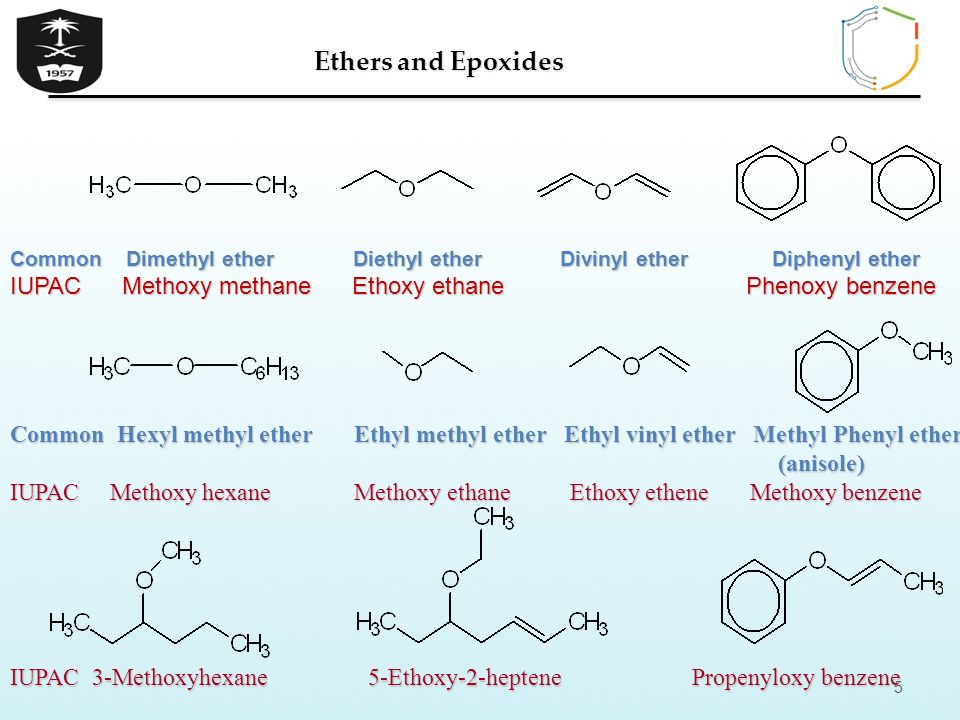
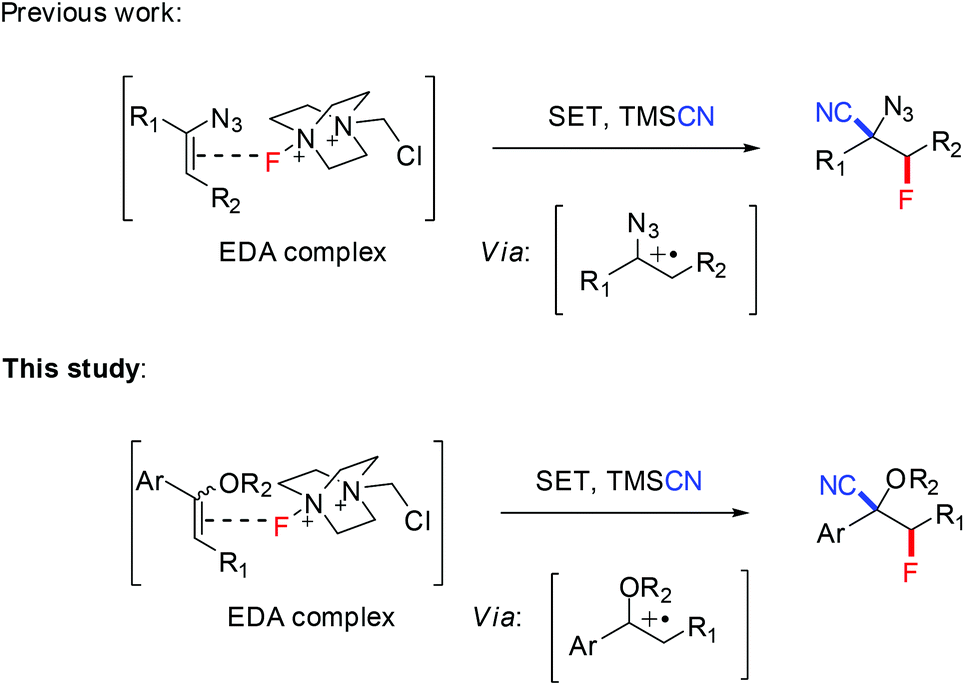
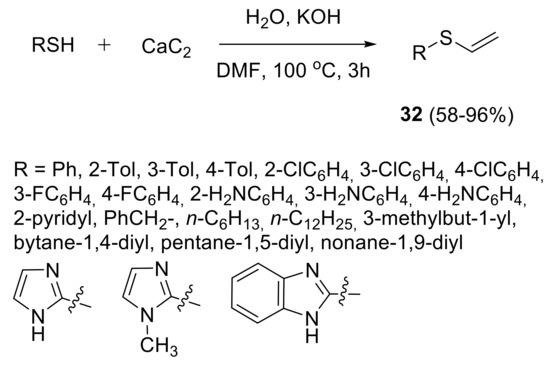
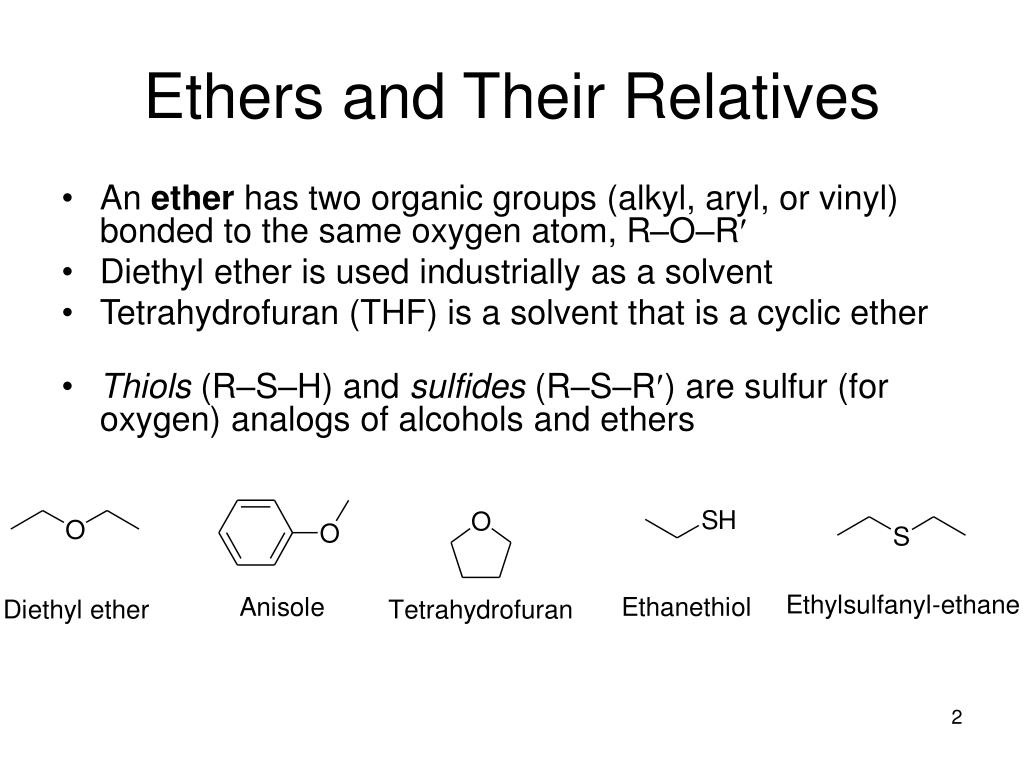
Vinyl Ethers Materials
In this work we have developed a versatile and highly efficient initiation approach based on thienyl chloride derivatives with readily available starting materials for the living cationic polymerization of vinyl ethers.
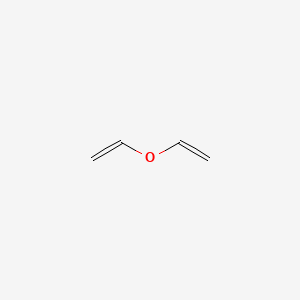
Vinyl ethers materials. Vinyl ethers are well established as radiation curable materials exhibiting a wide diversity of chemistry 1. Their glass transition temperature is well below room temperature. Vinyl ethers 1 which have a strongly electron donating alkoxy substituent readily form polymers on treatment with an acidic compound initiator. Vinyl ethers undergo radical initiated copolymerization in the presence of specific monomers such as maleates fumarates and acrylics.
Poly vinyl ether s pves are useful materials of different applications. A good selection of reactive monomers and prepolymers is commercially available. They are increasingly used in radiation curing systems because of a lower toxicity profile than the commonly used acrylic monomers. These materials possess several attractive features such as low toxicity and high reactivity.
Materials and equipment where as the low molecular weight mono functional vinyl ethers are mainly used as industrial monomers for the production of poly vinyl ethers the difunctional vinyl ethers are used as cross linking agents or reactive diluents in uv curable applications. It is prone to polymerization leading to formation of polyvinyl ethers. Is used as raw material for weather resistant coatings and has a good record of use for bridges and. Add an oxygen into the monomer.
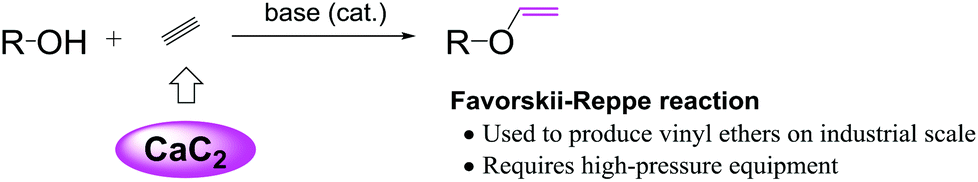
Vinyl ethers undergo homopolymerization via a cationic mechanism. The company started manufacturing in 1984 and remodeled facilities in 1996. The company has been manufacturing and selling vinyl ethers having a range of functions from low boiling point vinyl ethers to polyfunctionalized divinyl ethers. They also have fairly good.
For their elasticity and excellent resistance to hydrolysis being ether based pves do not hydrolyze. Polymerization is typically initiated with lewis acids such as boron trifluoride. Polyvinyl ethers are either viscous oils or soft and tacky rubbery materials depending on the structure and molecular weight.