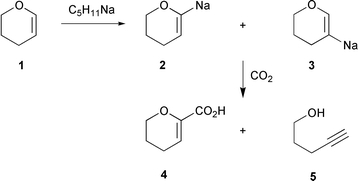
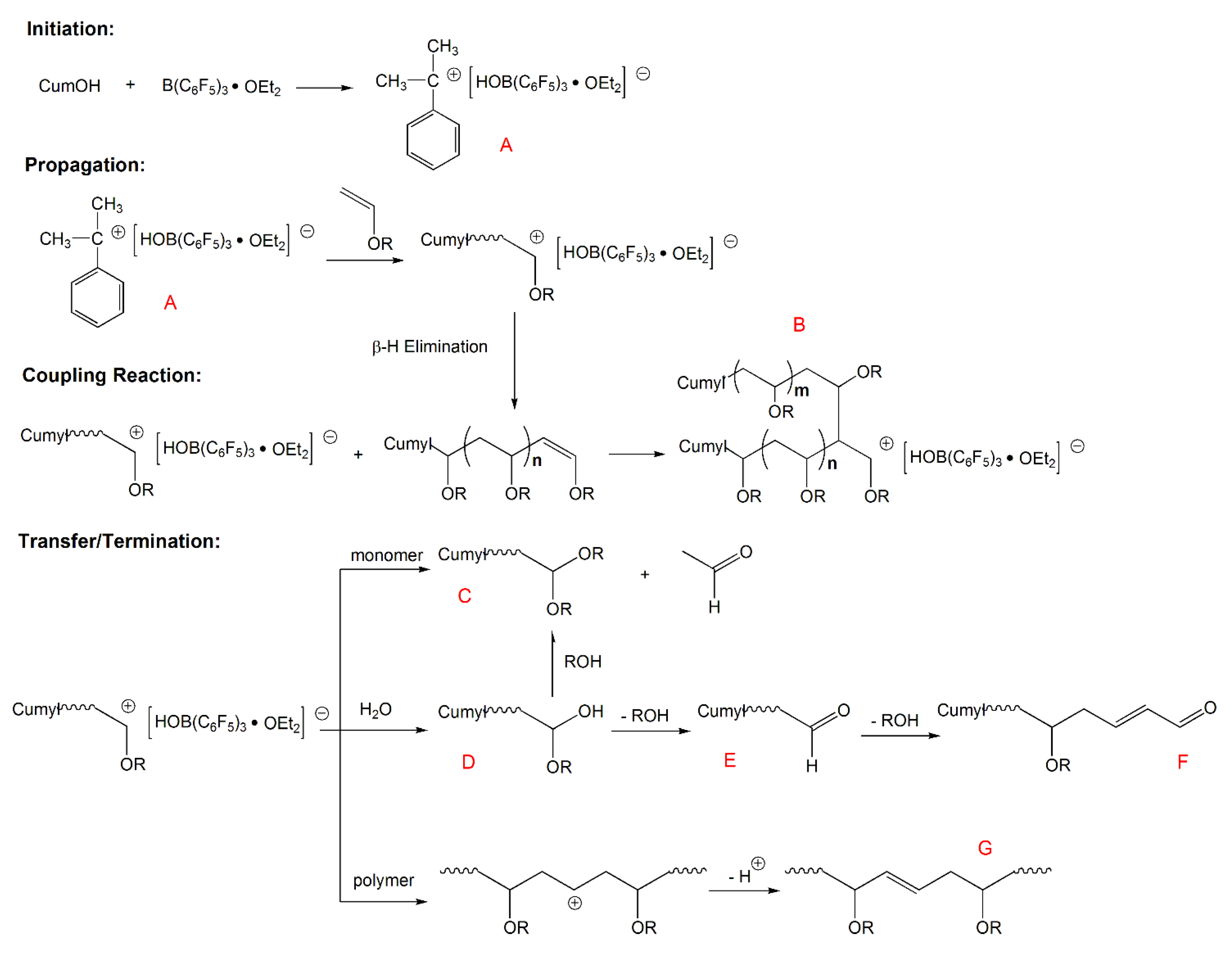
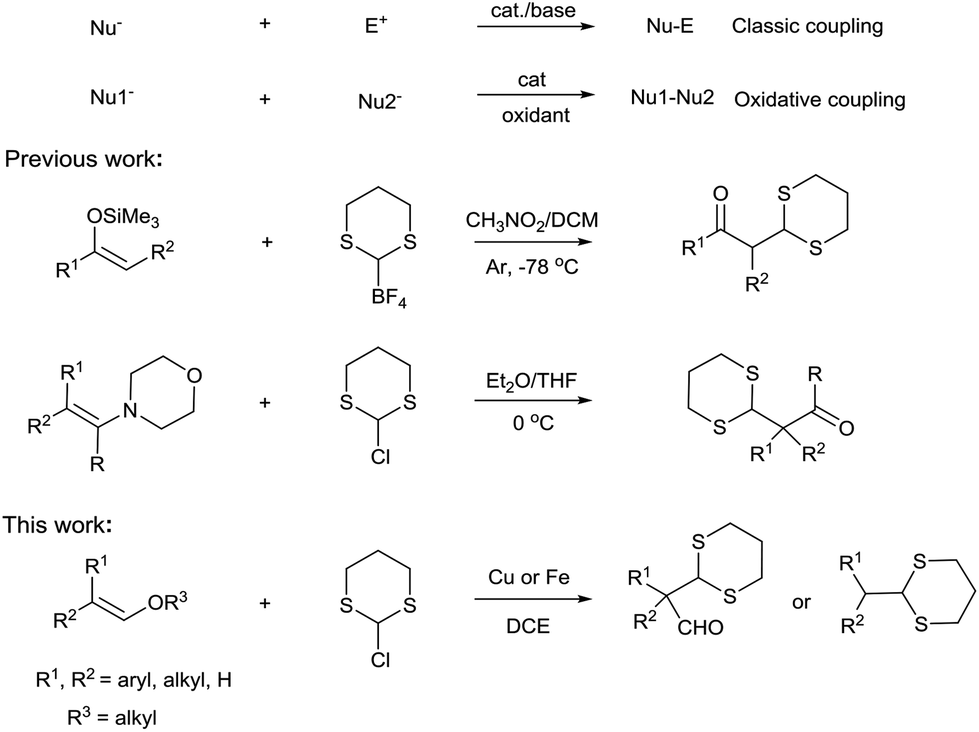
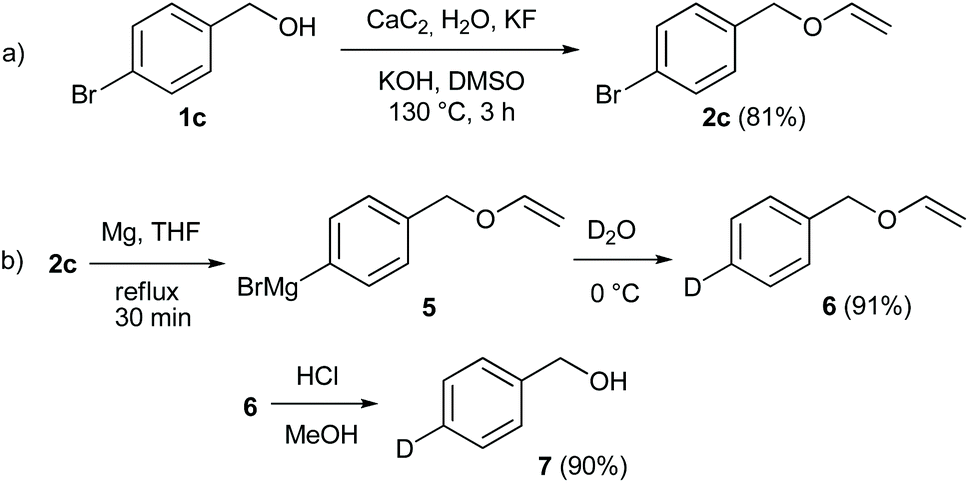
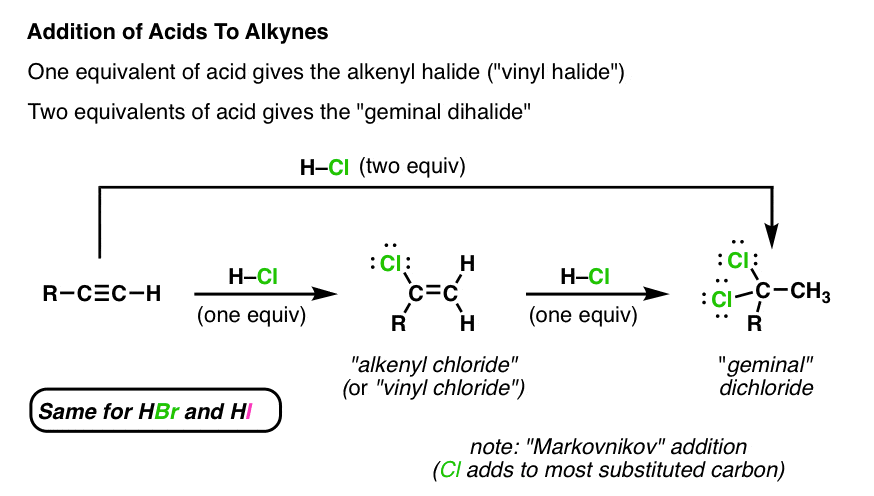Vinyl Ether Reactivity
Reacts possibly explosively with halogens bromine chlorine or hydrogen halides hydrogen bromide hydrogen chloride baker 1980 p.
Vinyl ether reactivity. Its reaction with acrolein is the first step in the commercial synthesis of glutaraldehyde. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat flame or strong oxidizing agents. In other reactions which typically involve the breaking of the carbon oxygen bond ethers are relatively inert. The complex between diethyl ether and boron trifluoride is an example.
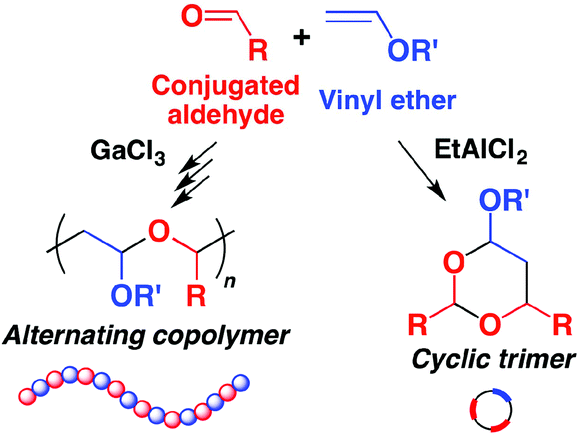
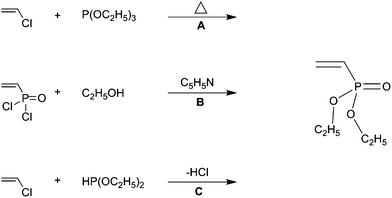
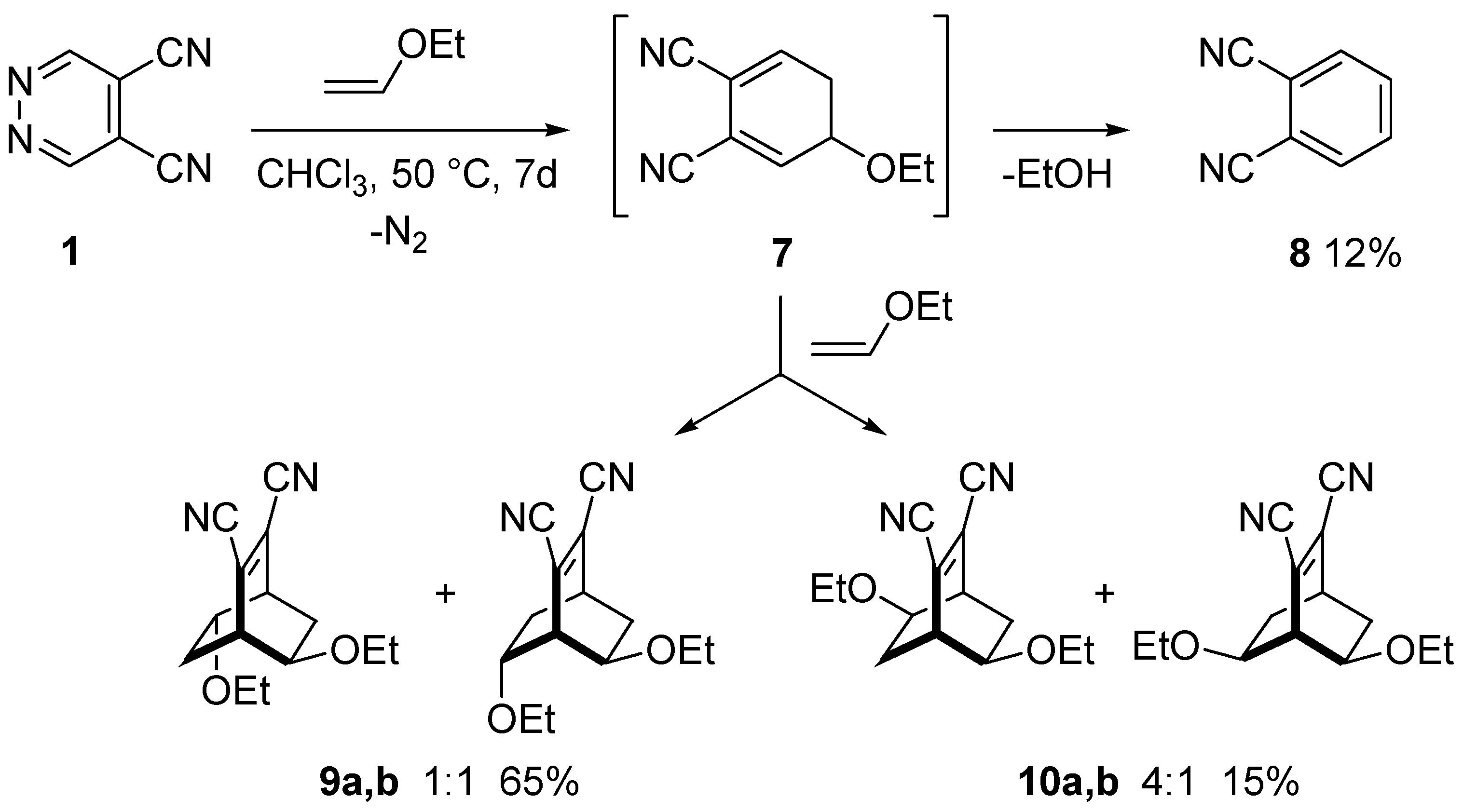
A good selection of reactive monomers and prepolymers is commercially available. Ethyl vinyl ether is made by reaction of acetylene and ethanol in presence of a base. A study has been made of the reactions of 2 vinyloxyethanol 1 2 divinyloxyethane ethyl vinyl ether and acetaldehyde ethyl 2 hydroxyethyl acetal with ethylene glycol and with diethylene glycol when heated and also in presence of catalysts concontrated hcl. 2 2 allyl ether substrates.
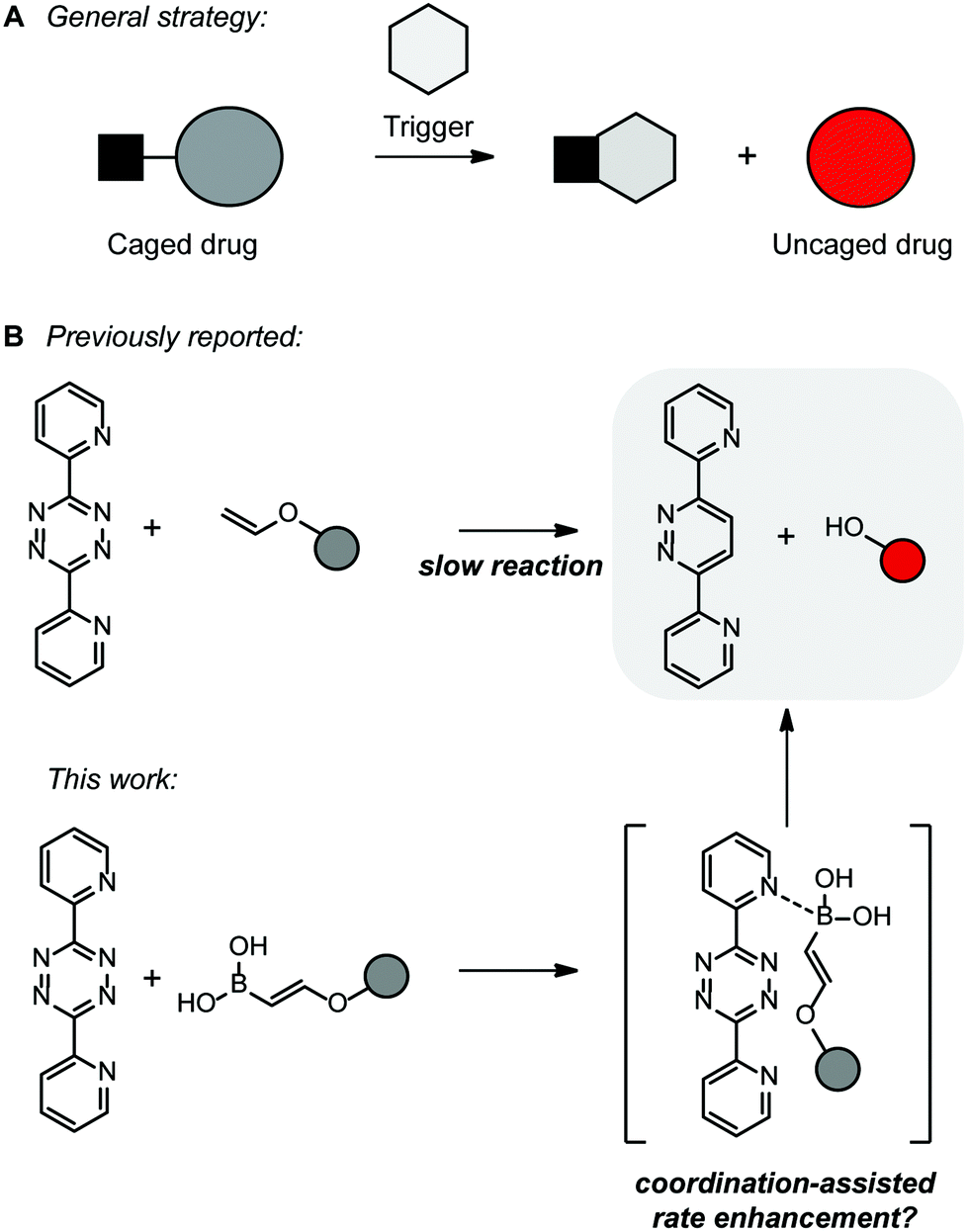
The vinyl carbonate 13 152 gives only copolymerization the ketene acetal 11 153 and the methyl vinyl ether 14 152 give both copolymerization and chain transfer in styrene polymerization whereas with the benzyl vinyl ethers 12 153 15 8 and 16 18 151 chain transfer is the only reaction detected. 12 we first used commercial phenyl vinyl ether 1 a as a model compound and tetrazine 2 a to challenge our decaging hypothesis. Methyl vinyl ether also participates in 4 2 cycloaddition reactions. In fact the reactivity of the vinyl group with tetrazines has been detailed in organic synthesis 11 and such a reactive pair was very recently employed to visualize and detect rna under bioorthogonal conditions.
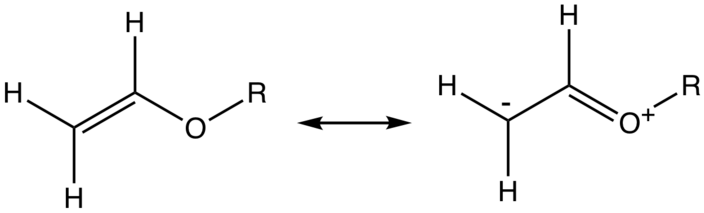
Ethers may react violently with strong oxidizing agents. It is prone to polymerization leading to formation of polyvinyl ethers. Vinyl methyl ether reacts vigorously with oxidizing materials. 2 modification of ethers.
This review presents the scope and limitations of these methods according to reaction type specifically via ether modifications elimination reactions carbonyl olefinations alcohol additions and carbon oxygen coupling reactions. Polymerization is typically initiated with lewis acids such as boron trifluoride. Vinyl ether monomers vinyl ethers are known for more than 100 years. This mode of reactivity is analogous to the way vinyl acetate and vinyl chloride can be polymerized to form polyvinyl acetate and polyvinyl chloride respectively.
The industrial production of vinyl ether monomers started in the 1930s based on the reppe reaction of acetylene with alcohols. It is miscible with alcohol acetone chloroform and ether and must be protected from light hawley. The alkene portion of the molecule is reactive in many ways. The cationic cure both uv and eb initiated of these materials is particularly rapid often.
It has been shown that both 2 vinyloxyethanol and the ethyl 2 hydroxyethyl acetal are extremely readily converted into the.