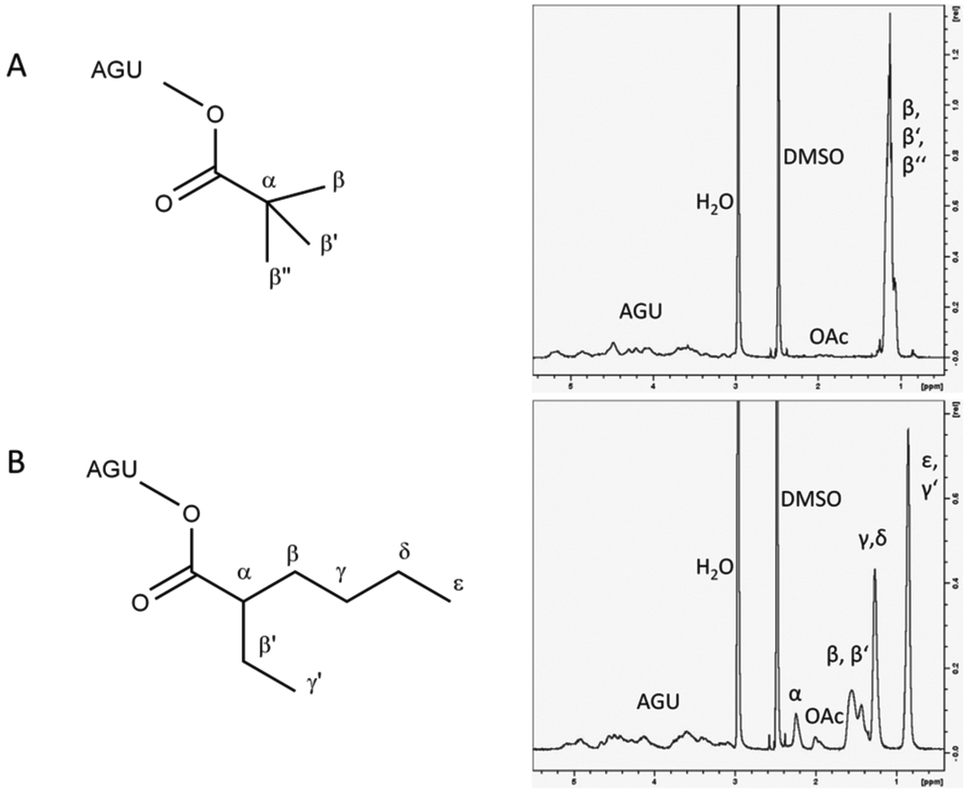
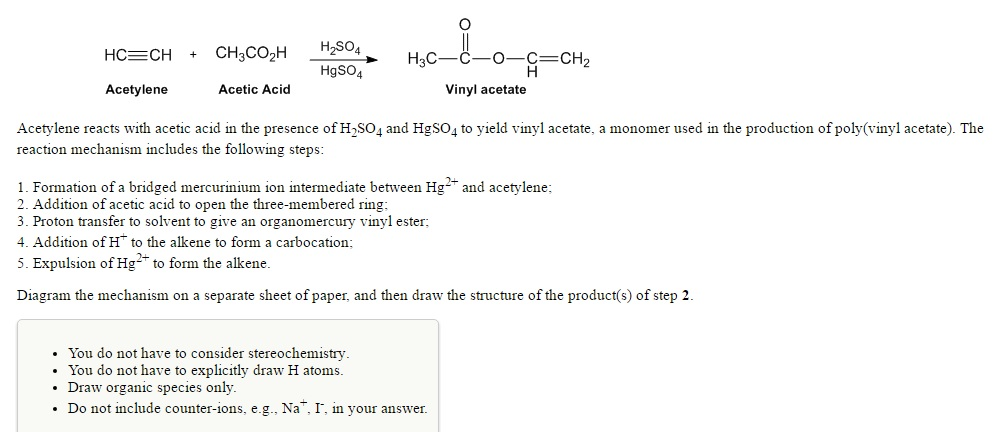
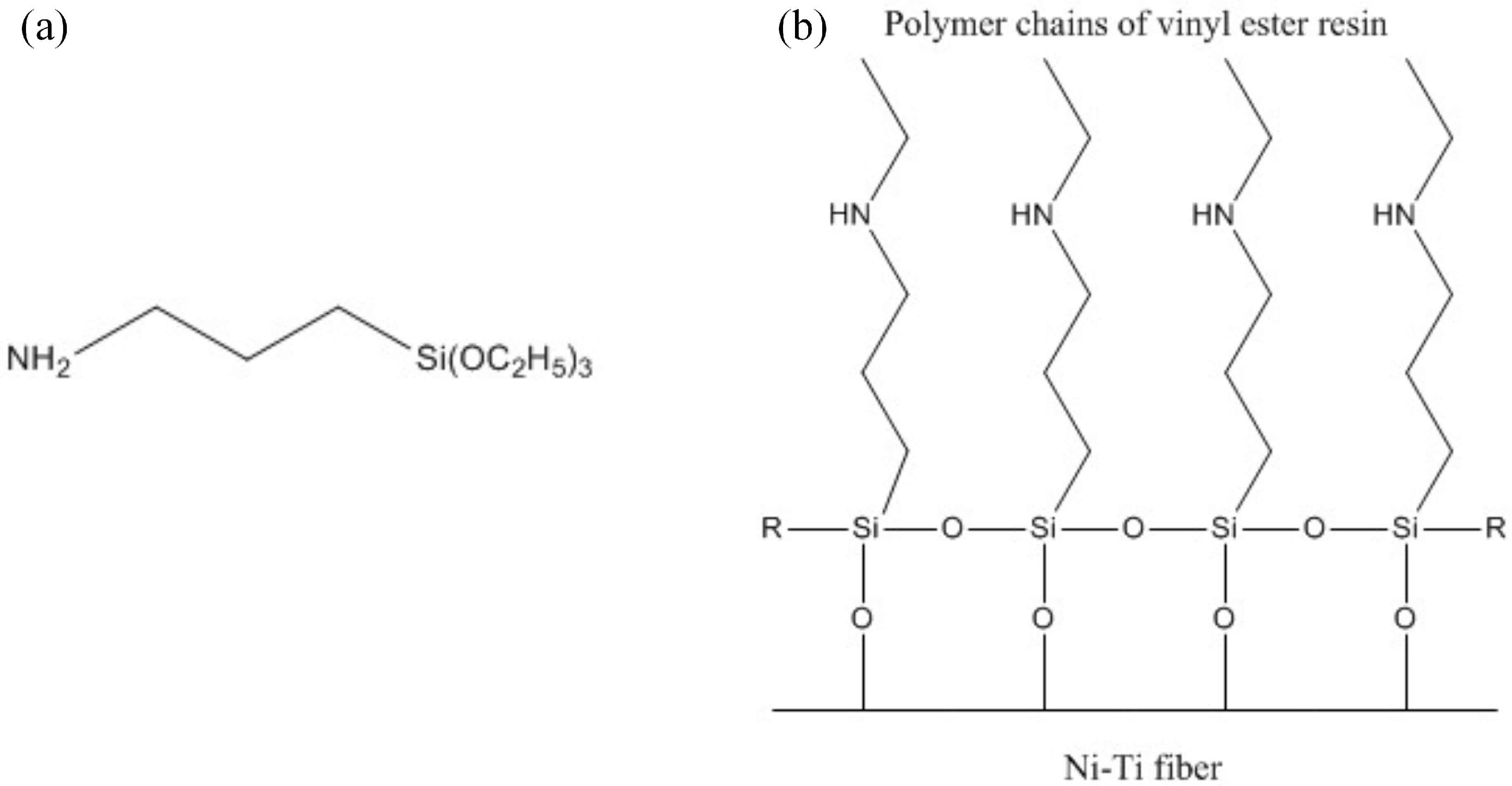
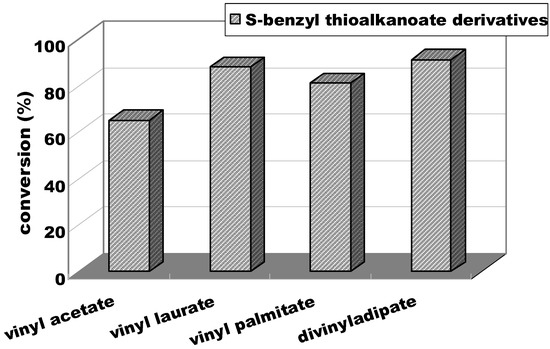
Vinyl Ester Structure

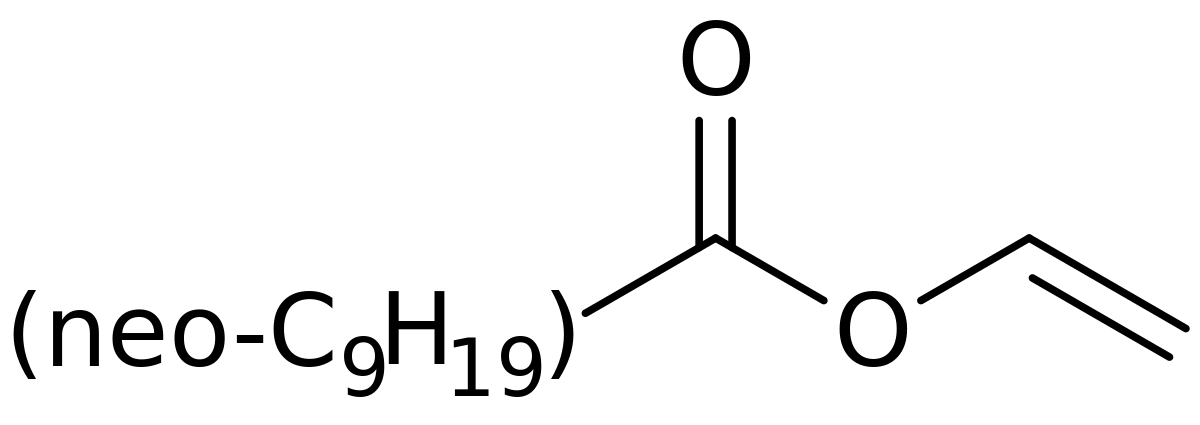
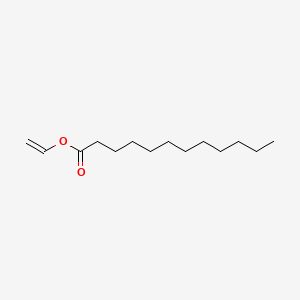
Benzoic acid ethenyl ester.
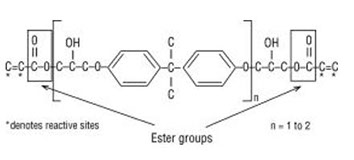
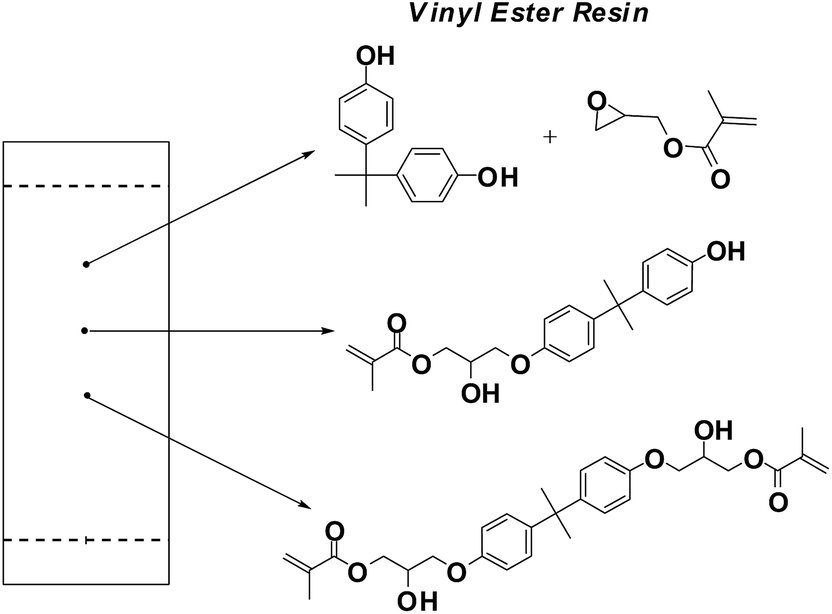
Vinyl ester structure. The vinyl groups refer to these ester substituents which are prone to polymerize. Vinyl ester monomer contains two vinyl end groups that allow cross linked structure to form during the reaction. The special chemical backbone of vinly ester resins prevent hydrolysis of ester groups. Unsaturation at the end of the structure provides for a full cure to obtain optimum properties.
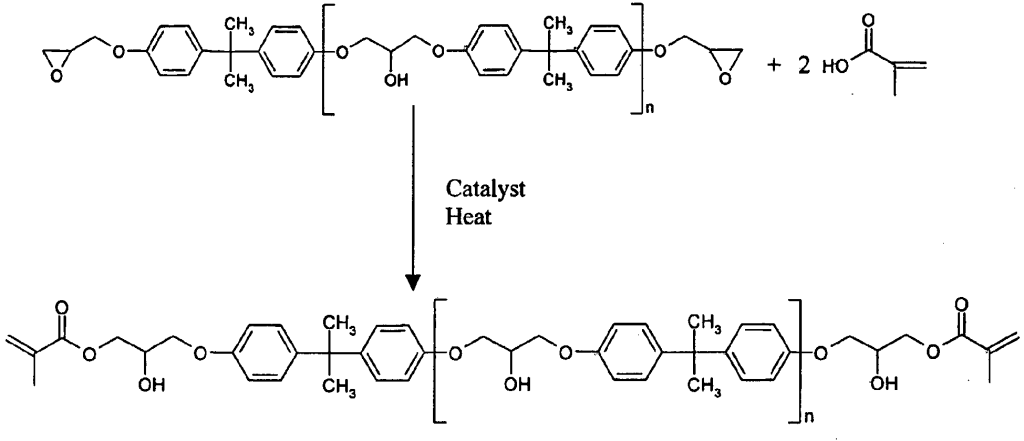
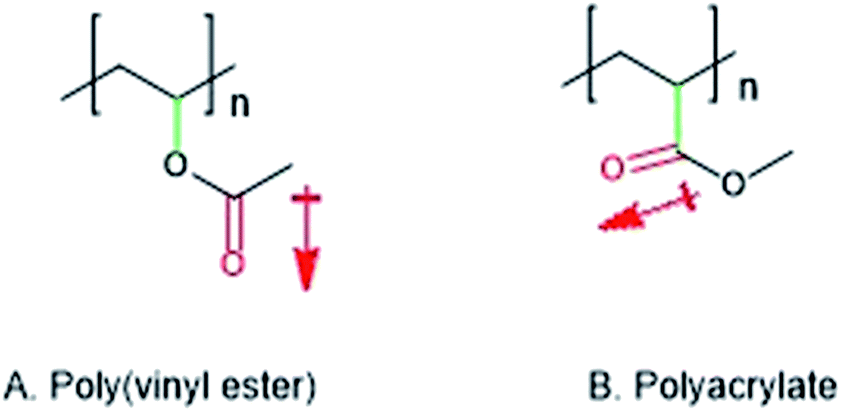
Vinyl ester oligomers diluted with styrene are important matrix resins for thermosetting polymer composites. Vinyl ester is dissolved in a monomer or reactive diluent usually styrene the result is a low viscosity liquid having a solids content of 36 39. Vinyl acetate is a commercially important monomer that is classified as a vinyl ester i e. Vinyl ester resin or often just vinyl ester is a resin produced by the esterification of an epoxy resin with acrylic or methacrylic acids.
As the whole length of the molecular chain is available to absorb shock loadings this makes vinylester resins tougher and more resilient than. Carbonic acid eicosyl vinyl ester c23h44o3 cid 91693137 structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature. Vinylester resins are similar in their molecular structure to polyesters but differ primarily in the location of their reactive sites these being positioned only at the ends of the molecular chains. Vinyl esters also use peroxides e g.
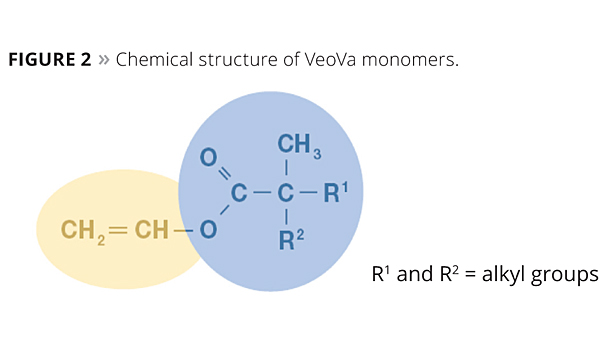
Benzoic acid vinyl ester. An ester of vinyl alcohol. Commercially important examples of these monomers are vinyl acetate vinyl propionate and vinyl laurate. Benzoic acid ethenyl ester 9ci benzoic acid ethenyl ester.
The diester product is then dissolved in a reactive solvent such as styrene to approximately 35 45 percent content by weight. A major objective of this work has been to study the chemistry and kinetics of the cure reactions of vinyl ester resins at elevated curing temperatures which are consistent with typical composite processing conditions. Vinyl ester resins are produced by the reaction esterification between an epoxy resin and an unsaturated monocarboxylic acid. Benzoic acid vinyl ester.
Polives resins special chemical backbone with hydroxyl functionality at the end of chain offers very good wetting of glassfibers carbon and aramide fibers. As the length of the chain is available to absorb impact loads this makes vinyl ester resins more durable and resilient than polyesters. The molecular structure of vinyl ester resins is similar to that of polyesters but differs primarily on the location of their reactive groups which are positioned only at the ends of the chains.