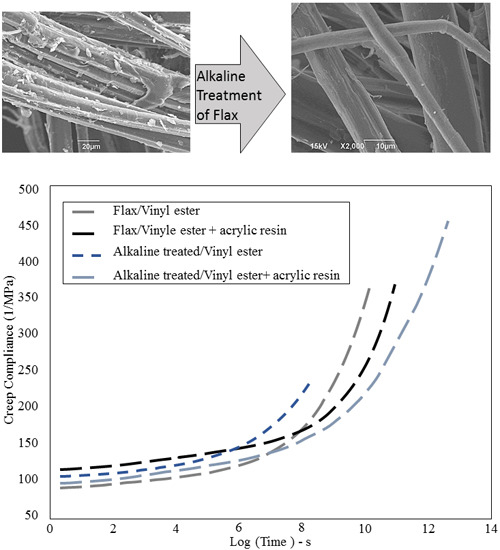
Vinyl Ester Resin Properties

Advances in fire retardant materials 2008.
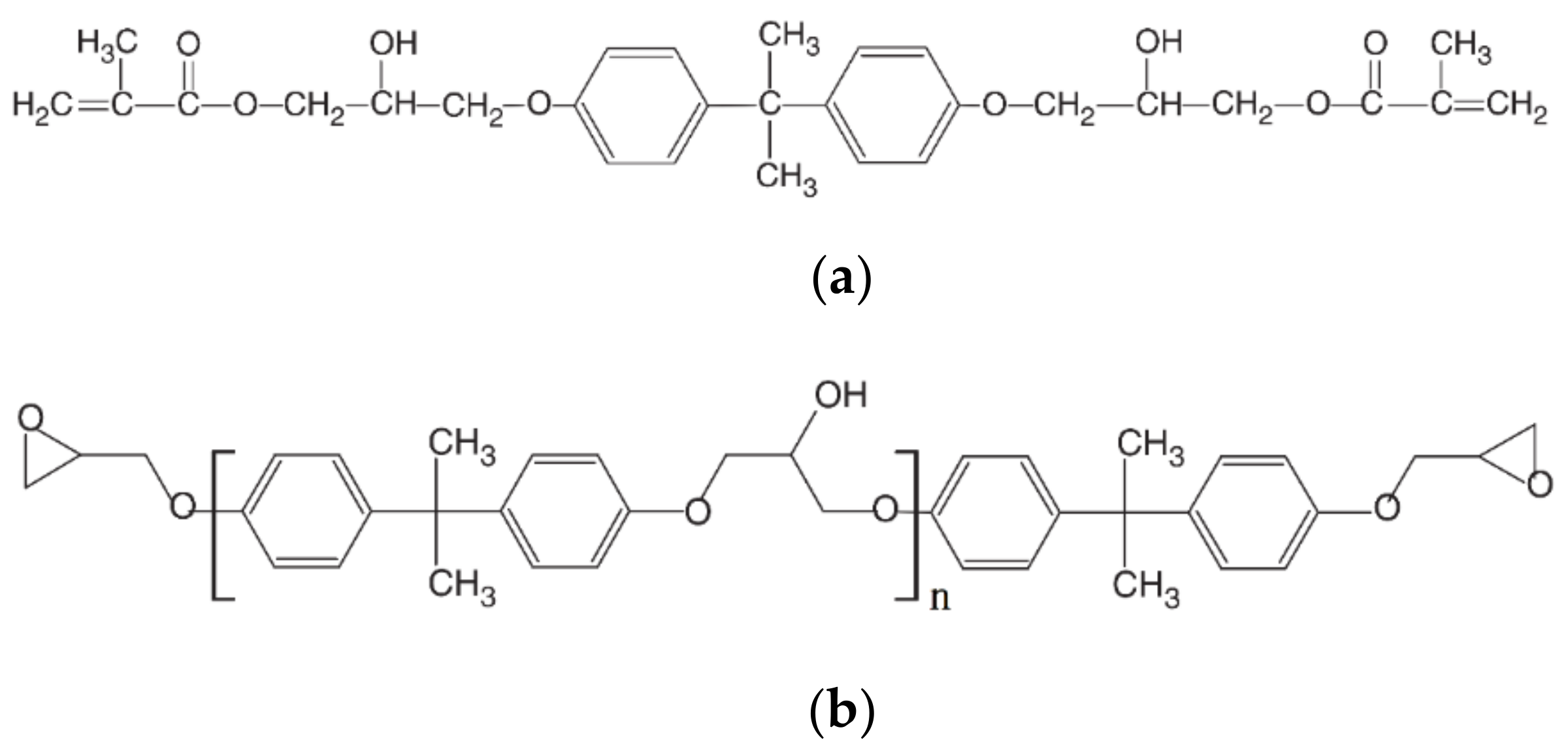
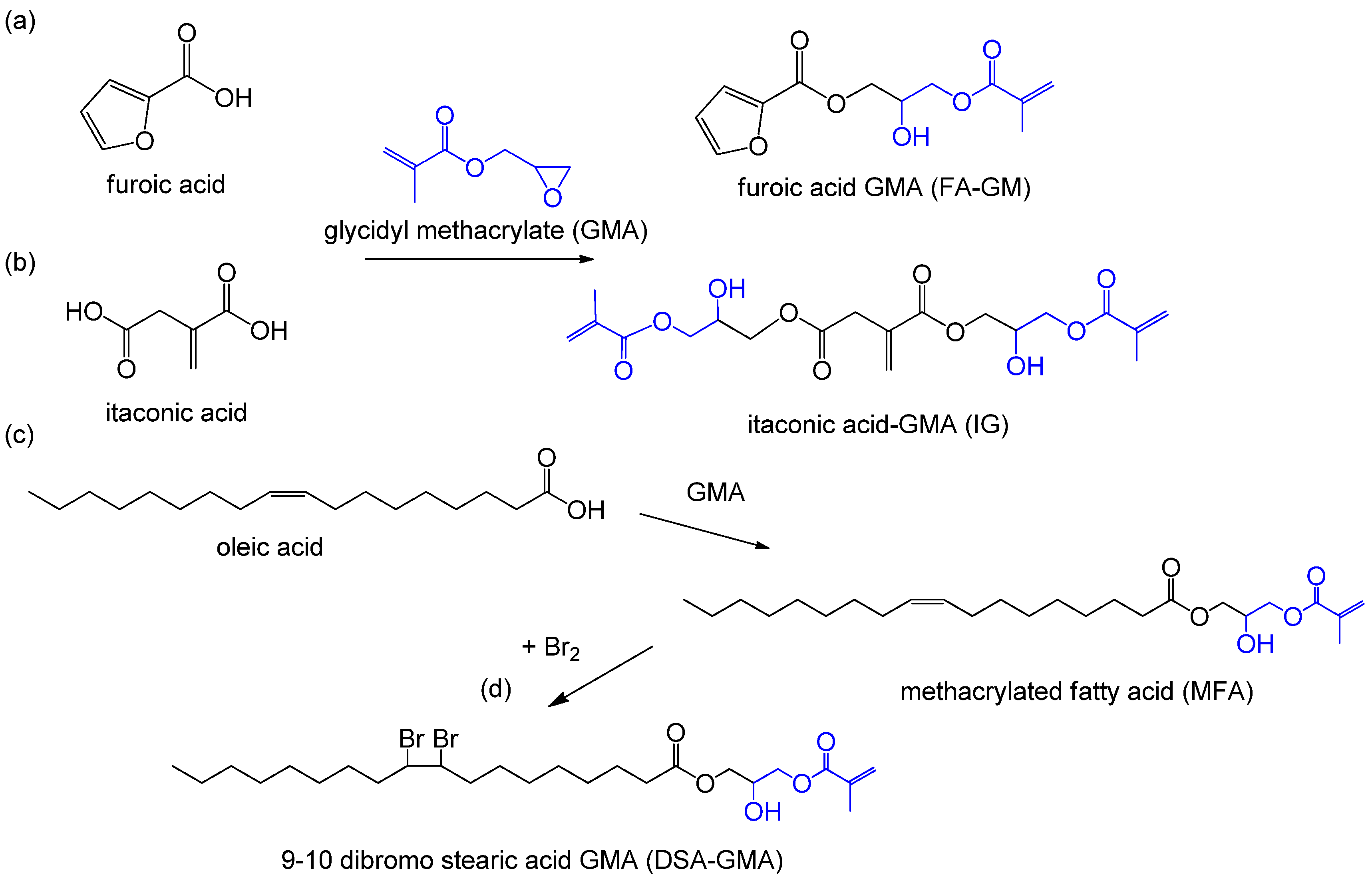
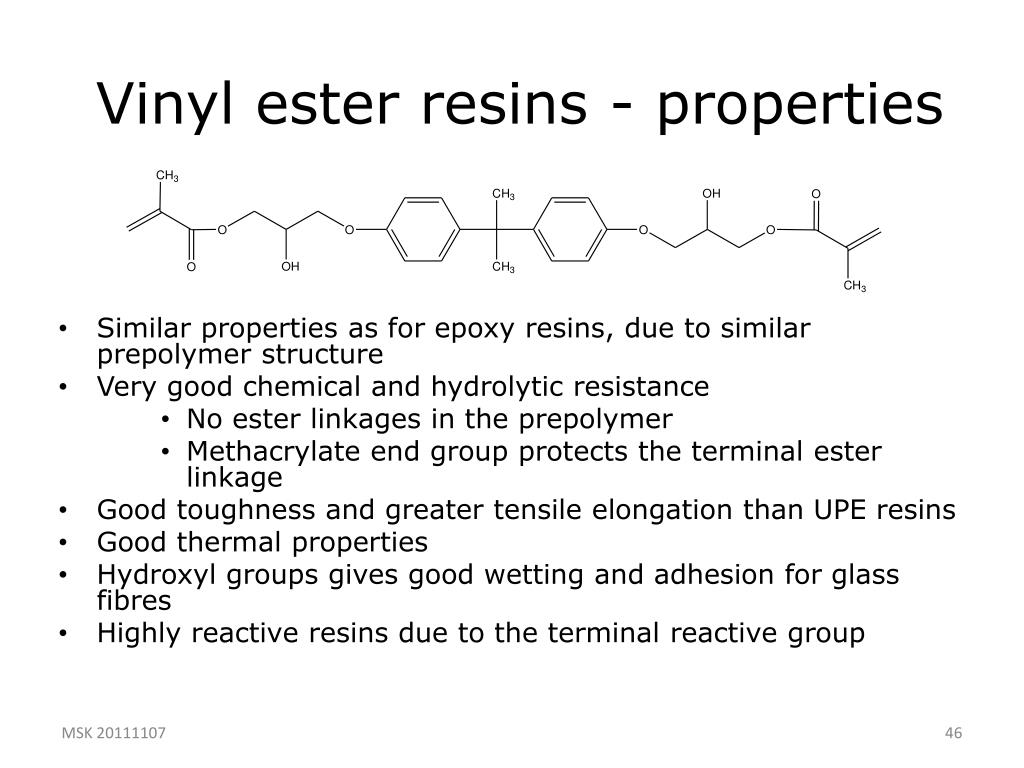
Vinyl ester resin properties. Essentially they comprise a base of polyester resin strengthened with epoxy molecules in the backbone of the molecular chain. Vinyl ester resins are produced by the reaction esterification between an epoxy resin and an unsaturated monocarboxylic acid. Vinyl ester resins vinyl esters are halfway between polyesters and epoxies as far as typical properties and toughness and they are a step up on a cost basis. They are produced by the addition of α β unsaturated carboxylic acids to epoxy resins.
Resins are bisphenol a diglycidyl ether dgeba and epoxy phenol. Vinyl ester resin vinyl ester resins are the binary resin systems containing a dimethacrylate monomer from which the cured material gains most of its properties and a reactive monomer such as styrene which acts as a reactive diluent and also takes part in the cross linking reaction. Standard epoxy vinyl ester resins are limited to 220 250 of 104 121 oc in most applications. Ve resins are a combination of both polyester resin and epoxy resins best properties.
Vinyl resins are often used in repair materials and laminating because it is waterproof and reliable. Renewable precursors to vinyl ester resins have been developed. Bisphenol a based epoxy vinyl ester resins provide high chemical resistance and mechanical strength. For laminating process vinyl ester is usually initiated with methyl ethyl ketone peroxide.
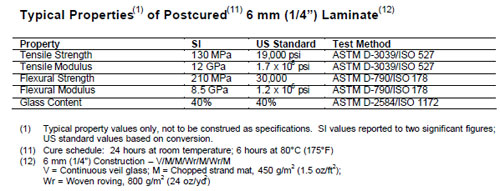
Vinyl esters also use peroxides e g. Properties epoxy vinyl ester resins ver are an important class of high performance thermoset molding resins. While they have high mechanical strength values similar to epoxy resins they are easy to apply similar to unsaturated polyester resins. Characteristics of vinyl ester resins and networks such as shrinkage viscosity crosslink density glass transition temperature gel swelling and toughness have been studied.
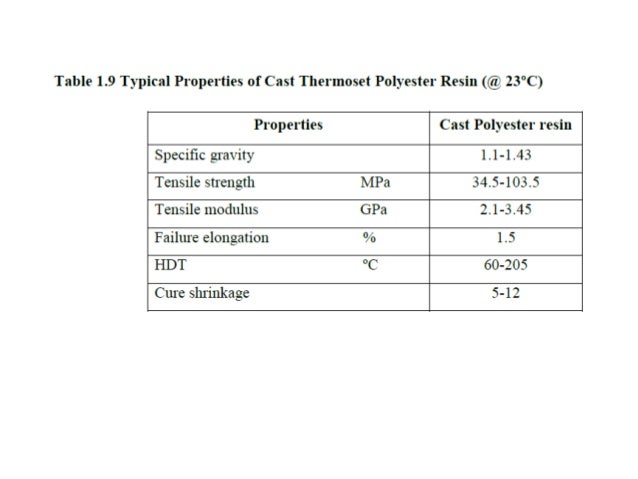
Vinyl esters have enhanced mechanical properties compared to polyesters with physical strength better impact and thermal shock resistance. The shrinkage of vinyl ester resins during cure was calculated according to density measurements to be 4 10 depending on styrene content. Vinyl ester resins offer increased strength corrosion resistance and durability and are used in a wide variety of applications. It has greater strength and mechanical properties than polyester and less than epoxy resin.
One of the key layers that has been introduced into fiberglass construction over the last 20 years has been the use of a corrosive resistant vinyl ester layer. While vinyl ester resins are classified as polyester based formulations they are actually an intermediate between a polyester backbone and epoxy terminations on the ends of the molecules.