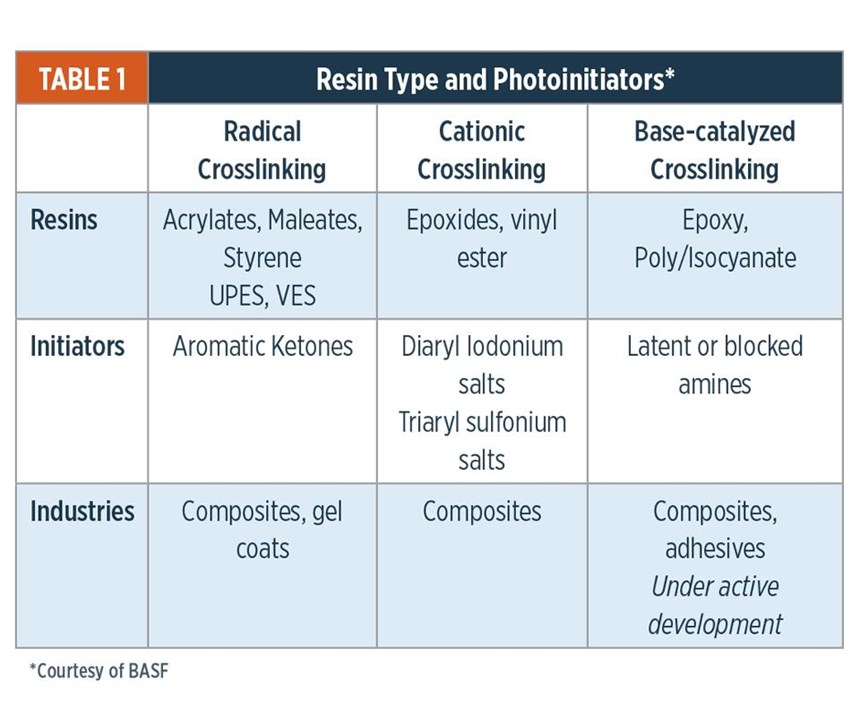
Vinyl Ester Resin Curing Temperature

0 13 mm to 0 400 in.
Vinyl ester resin curing temperature. Curing without addition of accelerators requires temperatures within the parts to be cured from approx. This is oversimplified but it does help convey the qualities of the resin. Resin and work area should be between 24 c 75 f and 35 c 95 f to ensure satisfactory results. About vinyl ester resins.
The cure time and pot life will depend on the initiator system its concentration as well as on the type of resin and vinyl monomer and cure temperature. Resin products with an activator are typically two pack systems whereas heat curable vers are typically one part systems. It is uv resistant which reduces yellowing and surface degradation from uv exposure. It has a measured glass transition temperature t g of 110 c hence allowing the clamp to withstand up to a maximum service temperature of 80 c.
Vinyl ester falls between polyester and epoxy on price most physical. It is ideal to work in temperatures around 77 degrees. The effects of isothermal temperature on the curing extent gel time dynamic rheological behaviors and mechanical properties of vinyl ester resins vers were systematically studied. The post cure at 60 c of the ve resin cured at 25 c also produces additional post curing and hydrolytic degradation because of the aging temperature is above the post curing temperature.
Like polyester resins they require mekp as a catalyst to cure or harden. Polymer chemistry curing ve resin 10 accelerator 553s in vinyl ester resin epoxy based vinyl ester 100 100 butanox m 50 phr 2 2 accelerator nl 51p 6 co soln phr 0 5 accelerator 553s 0 5 gassing geltime in pure resin min yes 60 no 60 cobalt content mg kg 300 100 time to peak min 113 108 peak exotherm c 44 61 barcol hardness. Although the curing extent was observed increase with increasing the operating temperature the study of residual heat of cured vers indicated that the final. Typical composites are made in thicknesses ranging from 0 005 in.
Vinyl ester resin is selected due to its well known performance in marine conditions and good chemical resistance to a wide range of chemicals including sour crude up to 100 c. The most common vinyl monomer is styrene. Previous work has shown that higher catalyst levels yield a higher degree of cure for thin panels made at 77 f 25 c. As with all polyesters rate and degree of cure are functions of catalyst concentration and of temperature.
Vinyl ester resins are often considered a cross between polyester resins and epoxy resins. Mixing the correct ratio of a b is extremely important. These temperatures are necessary to achieve a reasonable degree of curing within a short time. However the aging of the ve resin post cured at 100 and 140 c does not change the chemical structure of ve resin as the aging is produced above the post curing temperature.
Complete cure of a resin is critical to achieving the optimum corrosion resistance and physical proper ties of a laminate.